A semiconductor is a unique substance with electrical conductivity that is neither as poor as insulators nor as easy as metals. It is ideal for electronic equipment because its conductivity is controllable. Silicon is the most widely used semiconductor and is found in solar panels, computers, and smartphones. We can alter its behavior and produce components like diodes and transistors by doping it with minute amounts of other elements. Electrical signals are amplified and controlled by these components. Modern technology relies heavily on it, which enable gadgets to operate more quickly, consume less energy, and fit into smaller spaces. Many commonplace devices and cutting-edge technology would not be conceivable without semiconductors!
How to Made Semiconductor:
Start with Pure Materials-
- The most common material is silicon.
- Silicon is extracted from sand (silicon dioxide) and purified to be extremely pure—up to 99.9999999% pure!
Create a Silicon Crystal-
- To create a single crystal known as a silicon ingot, the purified silicon is melted and then gradually cooled.
- Wafers are extremely thin slices of this ingot.
Doping-
- Other elements, such as phosphorus or boron, are added in trace amounts.
- By altering the electrical characteristics, this process—known as doping—makes the material either p-type or n-type.
Fabrication of Components-
- Patterns are printed onto the wafers using processes like as photolithography.
- To construct circuits such as transistors, diodes, etc., layers of metals and insulators are added.
Testing and Packaging-
- Performance tests are performed on the semiconductor components.
- After that, they are linked, trimmed, and packed for use in electronic equipment.
How It Work:
- Conduction and Valence Bands: In the conduction band is empty, while the valence band, which is the outermost layer of electrons, is full.
- Electrons move from the valence band to the conduction band when a small amount of energy is applied. Electricity can pass through the material as a result of this movement.
- Doping for Improved Performance: We can alter the it’s electrical conductivity by introducing trace amounts of other elements.
- n-type: To improve conductivity, more electrons are introduced.
- p-type: “Holes”—areas where electrons are absent—allow current to flow.
Semiconductor Common Materials:
- Silicon (Si) – This is the most popular semiconductor material. It’s used in almost all electronics like computers, phones, and solar panels because it’s cheap, stable, and easy to work with.
- Germanium (Ge) – Though less common, germanium is used in special devices like infrared detectors and high-speed circuits because of its unique properties.
- Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) – This material is great for fast electronics and devices that use light, like LEDs and satellite communication systems. It’s more expensive but works well where speed and efficiency are important.
Uses of Semiconductor:

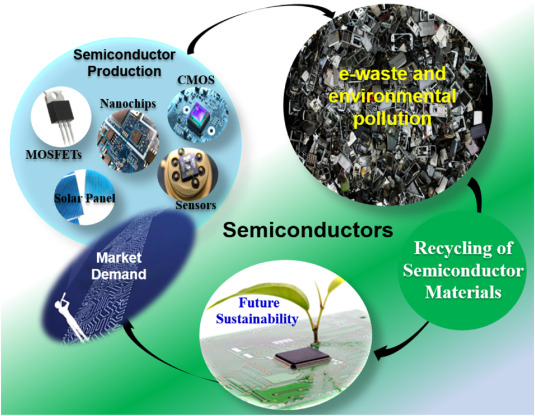
We encounter semiconductors on a daily basis! They speed up information processing in tablets, computers, and cellphones. Energy-efficient LED lights are powered by them. it is used by solar panels to convert sunlight into power. They aid in scanning and health monitoring in medical equipment. They are essential for improved performance and safety in cars, particularly electric ones. They are also essential to communication systems that keep us connected, such as satellites and the internet. Semiconductors are among the most vital materials in the modern world because most current technology would not function without them!
- Diodes – Allow current to flow in one direction.
- Transistors – Amplify or switch electronic signals.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs) – The building blocks of computers and smartphones.
- Solar Cells – Convert sunlight into electricity.
- LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) – Used in displays and lighting.
Type of Semiconductor:
It mainly divided into two types based on their structure and how they conduct electricity-
1.Intrinsic Semiconductors-
- Pure Materials: Without any additional contaminants, pure, natural materials like as silicon or germanium are used to make intrinsic semiconductors.
- Temperature Affects Conductivity: Heat or cold affects their capacity to conduct electricity since electrons need energy to move.
- No Doping: In contrast to other varieties, the substance is pure and stable because nothing is blended into it.
- Used in Basic Electronics: These are ideal for sensors and early-stage devices, which are examples of rudimentary electronic components that require a high degree of precision and purity.
2.Extrinsic Semiconductors-
- Doping is the process of introducing trace amounts of other elements to pure materials, such as silicon, to produce extrinsic semiconductors.
- Better Conductivity: The material conducts electricity more effectively than pure semiconductors thanks to these additional impurities.
- Two varieties:
- n-type: Phosphorus and other elements are used to add extra electrons.
- P-type: When elements like boron are added, “holes” are formed that permit electricity to pass.
- Used Everywhere: Due to their effective and dependable electrical control, they are present in practically all contemporary products, including laptops, smartphones, and solar panels.
Why Semiconductors are Important in India :
- Semiconductors are becoming crucial to India’s technological advancement and growth. Semiconductors are essential to making cellphones, electric cars, solar energy, and medical gadgets more effective and reasonably priced as consumer demand rises. Strong semiconductor industries contribute to job creation and economic growth, and India is striving to become a global center for electronics production. Semiconductors foster creativity and independence with developments in 5G, AI, and clean energy. They promote innovative research and development and lessen reliance on imports. By investing in semiconductors, India is able to meet future technological challenges and maintain its technological competitiveness while also enhancing the quality of life for citizens across.